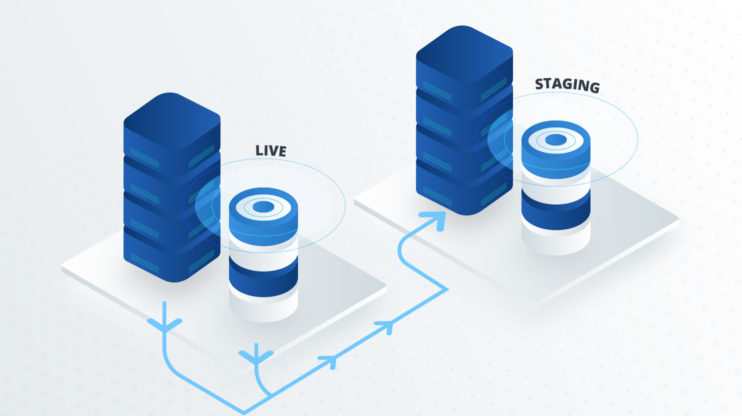
What is a staging environment?
A staging environment is essentially an exact replica of your website. It is where you can test changes, such as plugins, themes, and custom codes, without affecting your live website. Once you are done testing and the changes are to your satisfaction, you can push the staging environment to live. Alternatively, you can discard it.
When do you need a staging environment?
The purpose of a staging environment is two-fold. First, you want to be able to see the changes you would like to make in a “draft” form to confirm you are satisfied with them before launching them live. Second, you want to make sure that all changes made—whether they be plugins or codes, are working as they should before going live. If not, you have the opportunity to troubleshoot and fix any lingering issues before unveiling the final result. If you have a website, a staging environment is important as it can eliminate—or significantly reduce—issues for your website visitors, resulting in a better user experience. And if you need to make any changes on the live (production) website, using a staging website is a good practice to reduce the risks associated with bugs or downtime as one mistake on a live site may crash it. When an agency or business that develops websites wants to show a prospective client what to expect, a staging environment is also frequently used.
Pushing to live
When you are happy with all the changes made in your staging environment and are ready for your live website to reflect those changes, it’s time to push your staging environment live. Pushing to live means that your staging environment will now be copied to the live environment and will overwrite your existing live site. It has usually been an all-encompassing process, with the staging environment replacing the live site entirely during the push. This means the database and all files (media, plugins, themes, etc.). There currently are some options available for selective pushes, where you can choose just the database, just the files, or both. The process may take a few minutes to complete. It is always a good idea to have a backup of your live website ready, just in case any issues arise.
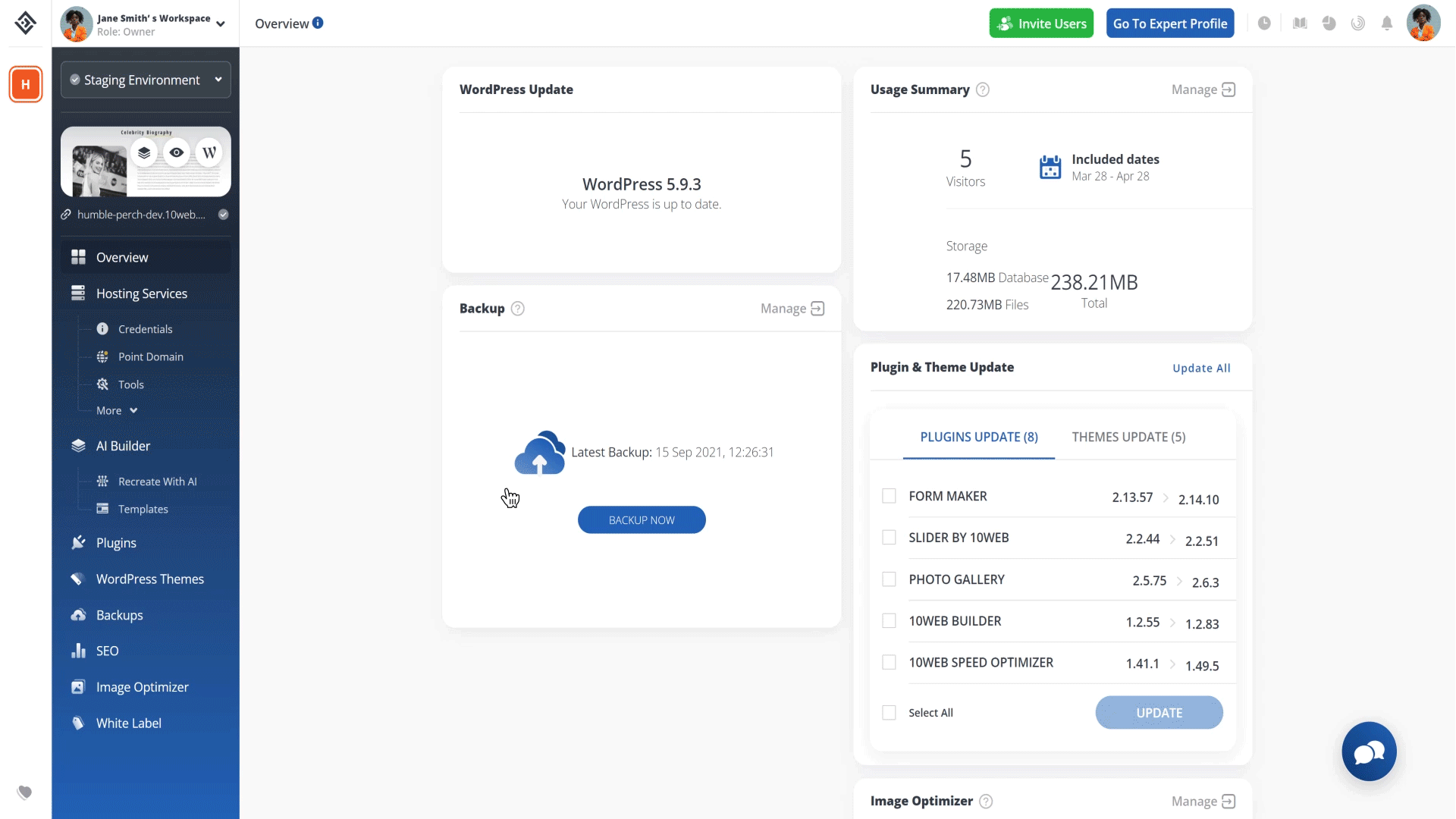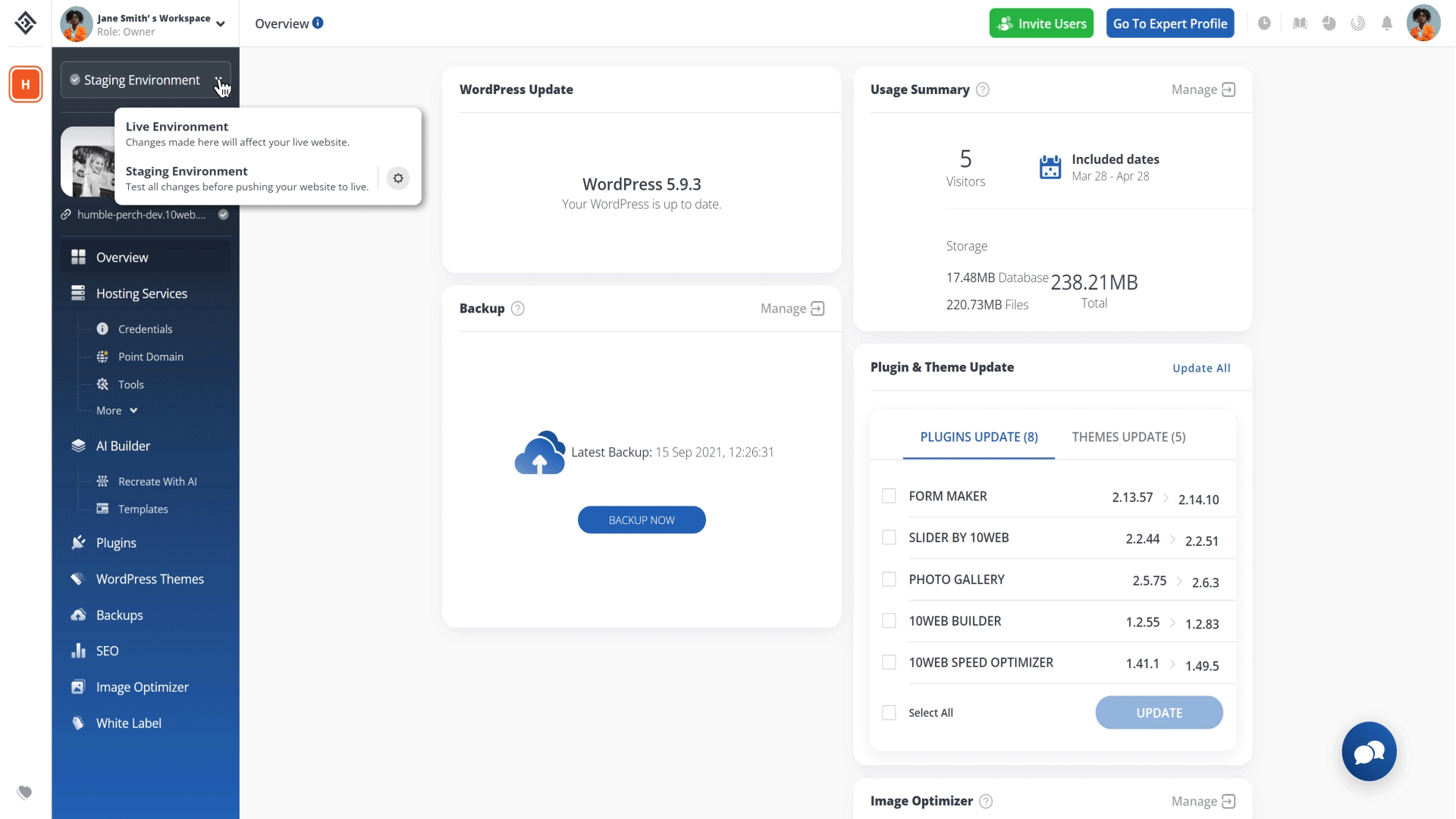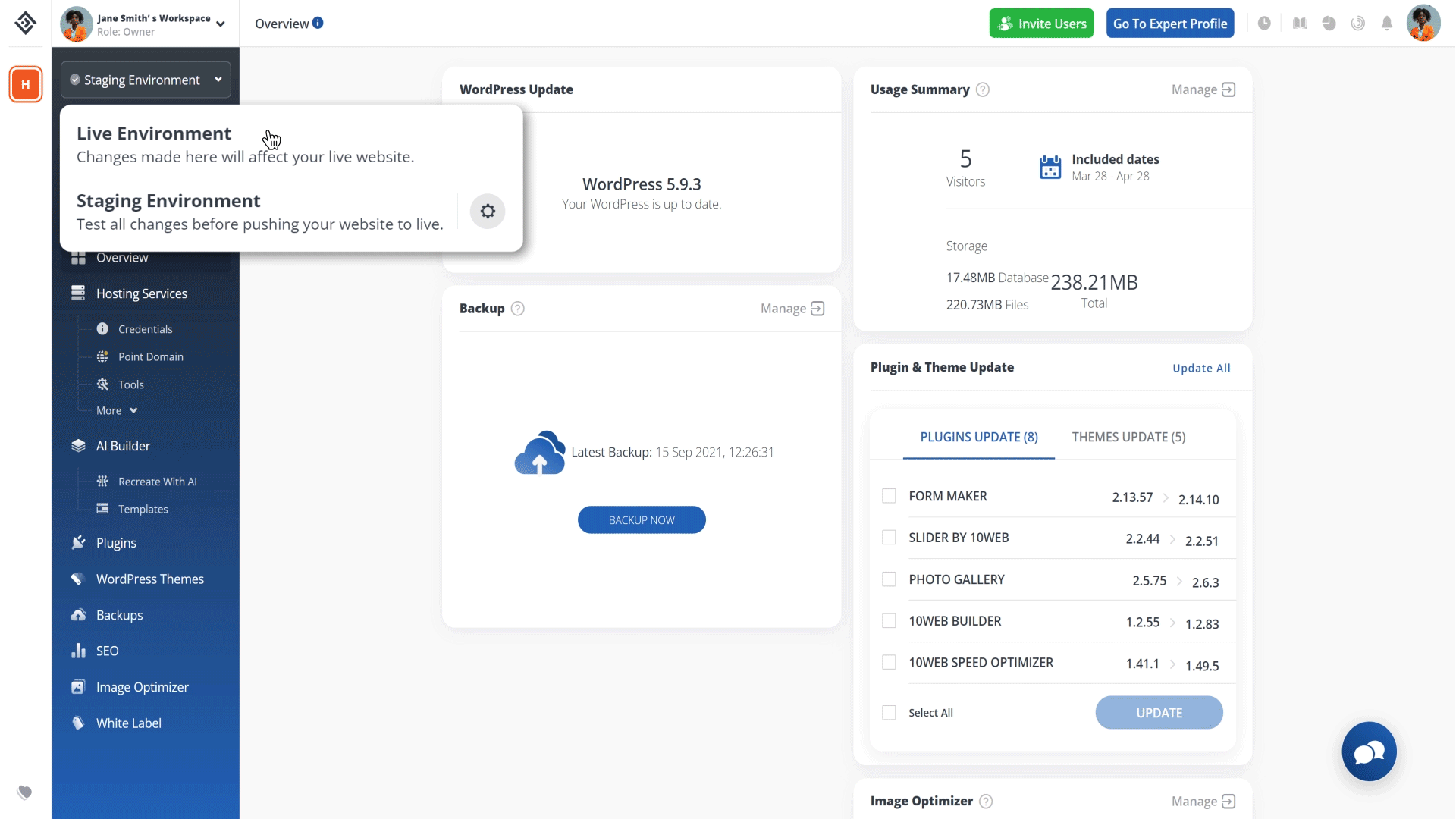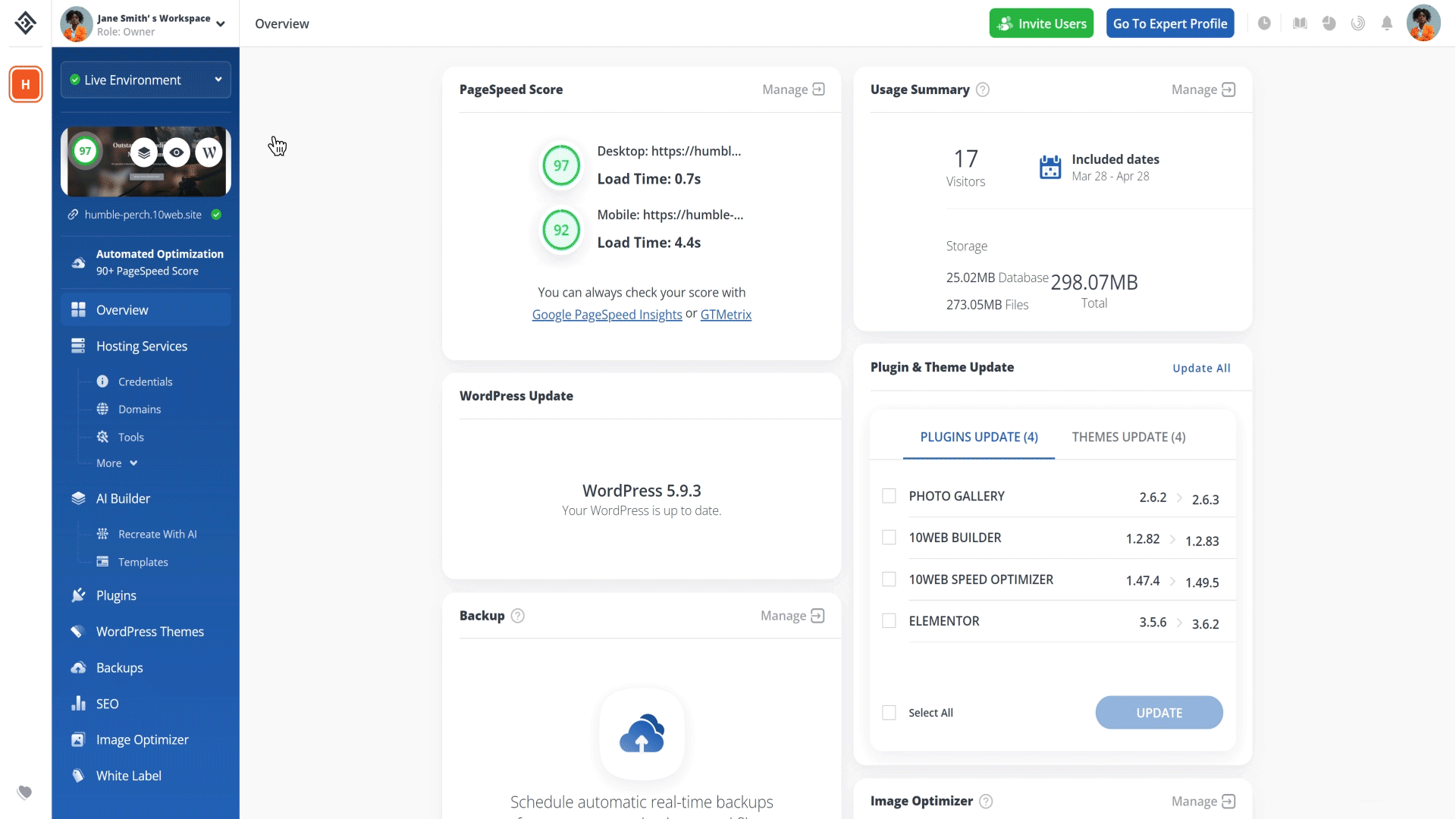
Syncing with live
Alternatively, if you’ve made some changes to your live website and would like your staging environment to reflect that so that later when you are pushing to live you do not break the changes here, you can choose to sync your staging environment (database, files) with the live one. This ensures you are testing changes on the most recent version of your existing (live) website.
What’s the difference between staging and live environments?
Staging websites are created for testing and development only so they don’t function properly as actual websites. A live environment, sometimes referred to as the production environment, is the version of the website that is visible to visitors. You can add custom access to staging websites, e.g. make it accessible only from your IP. Another difference when it comes to access is allowing, for example, a junior developer from your team access to only the staging site and not the live. Differences can also be found in optimizations, or other aspects such as debugging purposes.